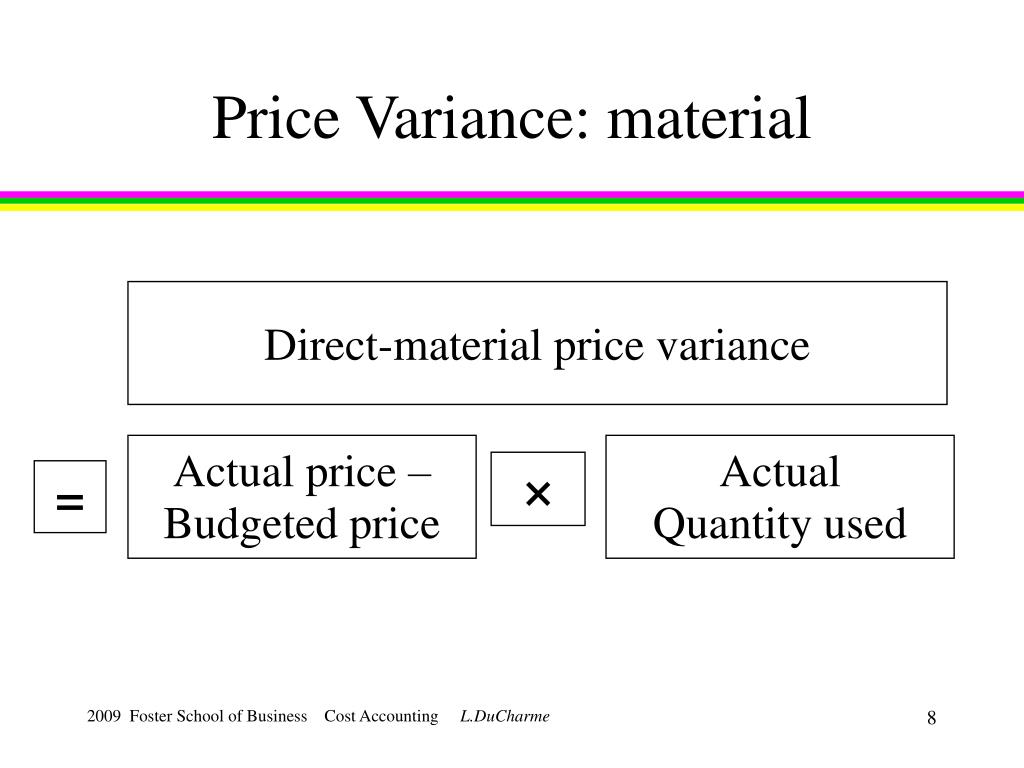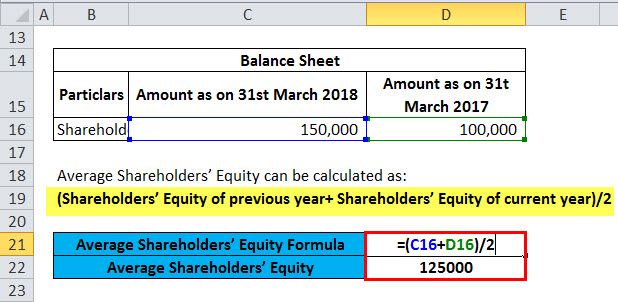
A high ROE can also indicate a reliance on debt to fund operations and growth, which can pose risks to the company’s financial stability. The average return on equity for the industry and the company’s past performance should be taken into account when calculating a company’s ROE. While a company may use debt to finance its operations, excess debt can lead to financial strain and lower returns. In the final step, we’ll calculate the return on equity (ROE) by dividing the “Net Income to Common” line item by the average between the prior and current period “Total Shareholders’ Equity”. One noteworthy consideration of the return on equity (ROE) metric is that the issuance of debt capital is not reflected since only equity is captured in the metric.
Interpreting ROCE Values
A high ROCE indicates that the company is generating substantial returns on its equity investment, while a low ROCE may signify inefficiency or suboptimal performance. Prudent investors take other factors into consideration before buying into a company such as earnings per share, return on invested capital, and return on total assets. ESG factors may impact a company’s profitability and performance in the long run and provide insights into the company’s social and environmental impact. Investors may also adopt customized benchmarks for different industries and businesses to reflect the specific operational and economic conditions. That being said, investors want to see a high return on equity ratio because this indicates that the company is using its investors’ funds effectively.
The Wharton Online & Wall Street Prep Applied Value Investing Certificate Program
Higher ratios are almost always better than lower ratios, but have to be compared to other companies’ ratios in the industry. Since every industry has different levels of investors and income, ROE can’t be used to compare companies outside of their industries very effectively. Due to variations in average ROCE ratios across industries, it is less suitable for cross-sector comparisons.
Return on Common Equity (ROCE) Formula
Ex’s ROCE of 16% indicates that for every dollar invested, a return of 16% can be expected from the company’s net income. If the industry average stands at 20%, Henry might reconsider his investment in Ex in search of better opportunities. This ratio provides valuable insights into the potential profitability of funds invested in a company. A high ROCE signals an enticing investment opportunity, whereas a low one should prompt caution among potential investors. While helpful, ROE should not be the only metric used to gauge a company’s financial health and prospects.
Return on Total Equity
- 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
- ROE provides insight into how well a company handles its investments to produce income.
- Therefore, investors should consider the impact of industry and economic factors on ROCE while analyzing a company’s financial performance and profitability.
- Understanding its risks and limitations is crucial for a clear and accurate assessment.
- Asset turnover measures how well a company uses its assets to produce revenue; the higher the asset turnover, the more efficient it is at generating revenue from its assets, enhancing the ROE.
To elaborate, Company A shows a higher ROE, but this is due to its higher debt, not greater operating efficiency. In fact, the company with the higher ROE might even suffer too much of a debt burden that is unsustainable and could lead to a potential default on debt obligations. The more debt a company has raised, the less equity it has in proportion, which causes the ROE ratio to increase. Similarly, ABC Manufacturing achieved an ROCE of 20%, demonstrating its ability to generate returns for its equity investors. My Accounting Course is a world-class educational resource developed by experts to simplify accounting, finance, & investment analysis topics, so students and professionals can learn and propel their careers. That’s why to gain a 360-degree view of a company’s efficiency, ROE must be viewed in conjunction with other factors, like ROA and ROI.
Note that the net income value should be taken prior to any issuance of dividends to common shareholders, as those payments impact the return to common equity shareholders. Meanwhile, the preferred dividends, which receive debt-like treatments, should be deducted from net income. The process of calculating the return on equity (ROE) is relatively straightforward, as it divides net income by the average shareholders’ equity balance in the prior and current period. As you can see, after preferred dividends are removed from net income Tammy’s ROE is 1.8.
For instance, technology firms may demonstrate higher ROE ratios than utility companies, indicating a more robust potential for growth and returns on equity in the tech industry. Benchmarking against industry averages aids in assessing a company’s performance how to prepare an income statement against its competitors. Return on Common Equity (ROCE) is a profitability ratio that showcases how effectively a company utilizes its equity to generate profits. It reveals the percentage return earned by common shareholders on their invested capital.
It indicates management’s efficiency in converting shareholders’ investments into earnings, which can be a positive sign to investors looking for companies with strong operational capabilities. Return on equity is a common financial metric that compares a company’s income to its total shareholders’ equity. Return on Equity (ROE) is an important financial metric that can be used to gauge a company’s profitability and efficiency in generating profits from the common shareholders’ investments. The return on common stockholders equity ratio, also known as ROE, is a vital metric used for evaluating a company’s financial health.